# 1. 前言
双向链表和单向链表的区别在于,在链表中,一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接,而在双向链表中,链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向前一个元素,如下图所示:
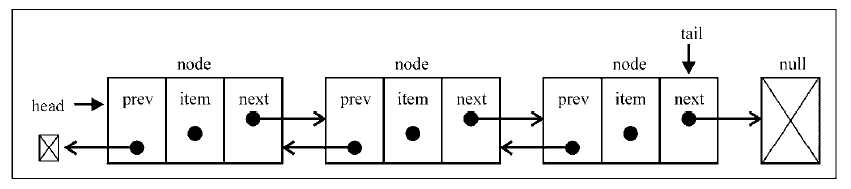
从图中可以看到,双向链表中,在每个节点 Node 里有 prev 属性(指向上一个节点的指针)和 next 属性(指向下一个节点的指针),并且在链表中也有 head 属性(用来存储链表第一项的引用)和 tail 属性(用来存储链表最后一项的引用)。
# 2. 代码实现
首先,我们可以先创建一个双向链表 DoublyLinkedList 类:
//创建一个Node辅助类,用来生成节点
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
append(element) {}
find(value) {}
insert(position, element) {}
remove(value) {}
removeAt(position) {}
size() {}
isEmpty() {}
nextPrint() {}
prevPrint() {}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
在创建 DoublyLinkedList 类时,我们还需要创建一个 Node 辅助类。Node 类表示要加入链表中的项。它包含一个 value 属性,即要添加到链表中的值,一个 next 属性,即指向链表中下一个节点项的指针,以及一个 prev 属性,即指向链表中上一个节点项的指针。
DoublyLinkedList 类也有存储链表项的数量的 length 属性(内部/私有变量)。
我们还需要存储第一个节点和最后一个节点的引用。为此,可以把这两个个引用分别存储在 head 和 tail 的变量中。
此外,DoublyLinkedList 类中还包含了如下一些方法:
- **append(value):**向链表尾部追加一个新元素
- **find(value)😗*根据元素值查找元素,并返回该元素
- **insert(position, value):**向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
- **remove(value):**根据元素值删除元素,并返回该元素
- **removeAt(position):**根据元素位置删除元素,并返回该元素
- **isEmpty():**判断链表是否为空,是返回 true,否返回 false
- **size():**返回链表包含的元素个数
- **nextPrint()😗*顺序遍历打印该链表
- **prevPrint()😗*逆序遍历打印该链表
# 3. 具体方法实现
# 3.1 append(value):向链表尾部追加一个新元素
/**
* 向链表尾部追加一个新元素
* @param {} element 要追加的新元素
*/
append(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
let current = this.head;
if (!this.head) { //如果链表为空
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 3.2 find(value): 根据元素值查找元素,并返回该元素
/**
* 根据元素值查找元素,并返回该元素
* @param {*} value
*/
find(value) {
let current = this.head;
if (!this.head) { //如果链表为空
console.log("这是一个空链表!!!");
return null;
}
if (current.value == value) {
return current;
}
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
if (current.value === value) {
return current
}
}
console.log("没有找到该元素!!!");
return null;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 3.3 insert(position, value):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
/**
* 向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
* @param {Number} position 要插入的位置
* @param {*} element 要插入的新元素值
*/
insert(position, element) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
let index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //如果在第一个位置插入
if (!this.head) { //如果链表为空
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { //如果在最后一个位置插入
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else { //如果在中间任意一个位置插入
while (index < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
index++;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
this.length++;
return true;
} else {
console.log('该位置不存在!');
return false;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
代码说明:
向任意位置插入一个新元素,总共可归纳为三种情况:
在列表的第一个位置(列表的起点)插入一个新元素。如果列表为空,只需要把 head 和 tail 都指向这个新节点。如果不为空,current 变量将是对列表中第一个元素的引用。就像我们在链表中所做的,把 node.next 设为 current,而 head 将指向 node(它将成为列表中的第一个元素)。不同之处在于,我们还需要为指向上一个元素的指针设一个值 current.prev 指针将由指向 null 变为指向新元素。node.prev 指针已经是 null,因此不需要再更新任何东西。
在列表最后添加一个新元素。因为我们还控制着指向最后一个元素的指针(tail)。current 变量将引用最后一个元素。然后开始建立第一个链接:node.prev 将引用 current。current.next 指针(指向 null)将指向 node(由于构造函数,node.next 已经指向了 null)。然后只剩一件事了,就是更新 tail,它将由指
向 current 变为指向 node。
在列表中间插入一个新元素。通过迭代列表,直到到达要找的位置。我们将在 current 和 previous 元素之间插入新元素。首先,node.next 将指向 current,而 previous.next 将指向 node,这样就不会丢失节点之间的链接。然后需要处理所有的链接:current.prev 将指向 node,而 node.prev 将指向 previous。
# 3.4 remove(value):根据元素值删除元素,并返回该元素
remove(value) {
let current = this.find(value);
if (current == null) {
console.log("没有找到该元素!!!");
return null;
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
this.length--;
return current;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 3.5 removeAt(position):根据元素位置删除元素,并返回该元素
removeAt(position) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
let index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //如果删除第一个位置
head = current.next;
head.prev = null;
if (this.length === 1) { //如果链表中只有一个元素
this.tail = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { //如果删除最后一个位置
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
while (index < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
index++;
}
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.length--;
return current;
} else {
console.log('该位置不存在!');
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
代码说明:
从任意位置删除一个元素,总共也可归纳为三种情况:
从头部移除第一个元素。current 变量是对列表中第一个元素的引用,也就是我们想移除的元素。需要做的就是改变 head 的引用, 将其从 current 改为下一个元素
。但我们还需要更新 current.next 指向上一个元素的指针(因为第一个元素的 prev 指针是 null)。因此,把 head.prev 的引用改为 null(因为 head 也指向列表中新的第一个元素,或者也可以用 current.next.prev)。由于还需要控制 tail 的引用,我们可以检查要移除的元素是否是第一个元素,如果是,只需要把 tail 也设为 null。
从尾部最后一个位置移除元素。既然已经有了对最后一个元素的引用(tail),我
们就不需要为找到它而迭代列表。这样我们也就可以把 tail 的引用赋给 current 变量,接下来,需要把 tail 的引用更新为列表中倒数第二个元素(current.prev,或者 tail.prev 也可以)。既然 tail 指向了倒数第二个元素,我们就只需要把 next 指针更新为 null(tail.next= null)。
从列表中间移除一个元素。首先需要迭代列表,直到到达要找的位置。current 变量所引用的就是要移除的元素。那么要移除它,我们可以通过更新 previous.next 和 current.next.prev 的引用,在列表中跳过它。因此,previous.next 将指向 current.next,而 current.next.prev 将指向 previous。
# 3.6 isEmpty():判断链表是否为空,是返回 true,否返回 false
isEmpty() {
if (this.length === 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 3.7 size():返回链表包含的元素个数
size() {
return this.length
}
2
3
# 3.8 nextPrint(): 顺序遍历打印该链表
nextPrint() {
var current = this.head;
while (current != null) {
console.log(current.value);
current = current.next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 3.9 prevPrint(): 逆序遍历打印该链表
prevPrint() {
var current = this.tail;
while (current != null) {
console.log(current.value);
current = current.prev;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 4. 完整代码
完整代码请戳 ☞☞☞DoublyLinkedList (opens new window)
